
Can You Overdose on Vitamins? The Surprising Truth
You’ve probably heard that vitamins are good for you. They give your body essential nutrients to function properly and stay healthy. But can you have too much of a good thing? Turns out, it is possible to overdose on vitamins. Before you start popping supplements like candy, you’ll want to know the facts. While vitamins in moderation and through a balanced diet are beneficial, consuming too many vitamins can actually be harmful and even toxic. Despite the popular notion that you just pee out the excess, that’s not always the case. Some vitamins accumulate in your tissues and organs, potentially causing damage over time. The effects of overdosing range from minor issues like nausea or diarrhea to life-threatening problems like organ failure in extreme cases.
The moral of the story? More isn't always better when it comes to vitamins. Learn how much is too much for each essential vitamin and the surprising side effects of overdoing it. Your health depends on achieving the right balance.
Shop vitamins and supplements at Oceans Alive.
What Does It Mean to Overdose on Vitamins?
So what exactly does it mean to overdose on vitamins? Simply put, it means you've consumed too much of certain vitamins, usually by taking high-dose supplements.
While vitamins are essential nutrients we need in small amounts, more isn't always better. In high doses, some vitamins can actually be harmful or even toxic.
Fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K are more likely to cause overdose because your body stores the excess amounts in fat cells. Water-soluble vitamins like C and the B vitamins are less likely to cause overdose since your body excretes the extra amounts in urine.
Common symptoms of vitamin overdose include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, weakness, and headache. In severe cases, overdosing on vitamins A, D, niacin or iron can cause liver damage, bone pain, vision problems, and abnormal heart rhythms.
While the amounts needed to overdose vary by individual and vitamin type, as a general rule you should avoid taking more than 100% of the Daily Value for most vitamins. And if you're taking high-dose supplements for an extended time, you'll want to talk to your doctor about appropriate dosages and signs of overdose to watch out for.
The Most Common Vitamins Associated With Overdose
When it comes to vitamins, more isn't always better. In fact, several of the most common vitamins can be downright dangerous in high doses.
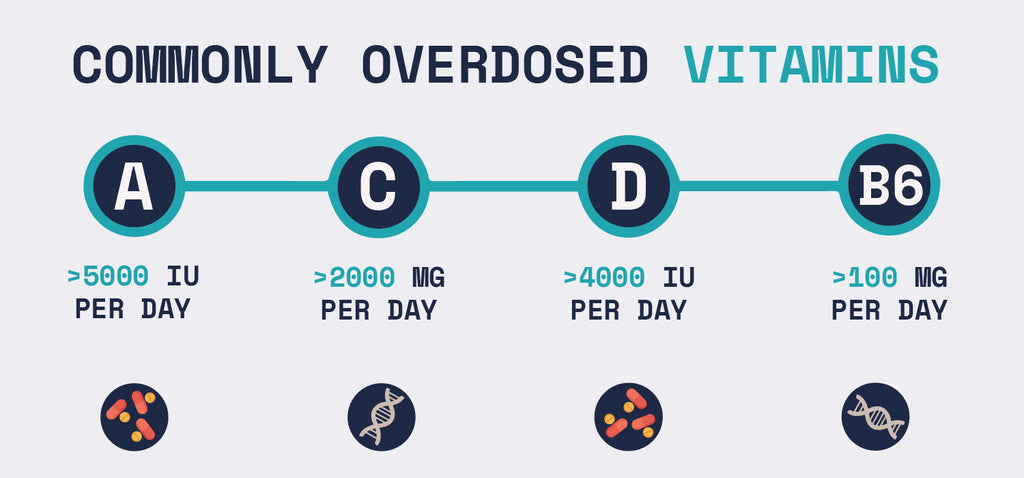
Vitamin A: Too much vitamin A can lead to nausea, irritability, and even liver damage. Stick to the recommended daily amount of 5,000 IU for most adults.
Vitamin D: While vitamin D deficiency is common, overdosing on supplements can cause confusion, vomiting, and kidney problems. Don't take more than 4,000 IU per day unless advised by your doctor.
Vitamin C: Vitamin C is water soluble, so excess amounts are typically flushed out in urine. However, mega-doses of 2,000 mg or more may lead to diarrhea, insomnia, and headaches. For most people, 60-90 mg per day is plenty.
Vitamin B6: High doses of B6, usually from supplements, can cause nerve damage leading to numbness, difficulty walking, and pain. The safe upper limit is 100 mg per day for adults. Talk to your doctor before exceeding the recommended amount of 1.3 mg.
The bottom line is moderation. While vitamins are essential for health, more is not always better. Only take higher doses of vitamins under the guidance of your physician to avoid potential overdose and side effects.
Signs and Symptoms of a Vitamin Overdose
If you consume too many vitamins, it can lead to toxicity known as hypervitaminosis. While vitamins are essential for health, too much of a good thing can be harmful. Some signs you may have overdosed on certain vitamins include:
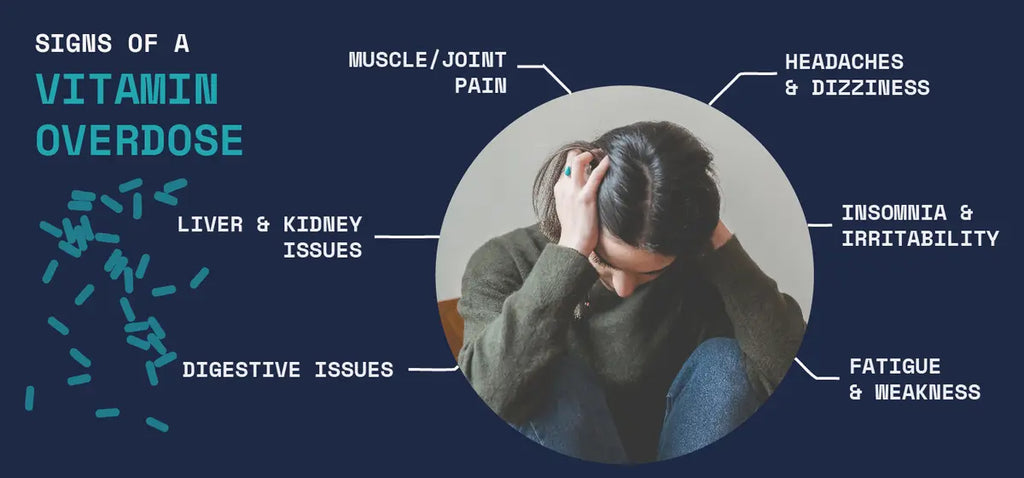
- Digestive issues: Too much vitamin C, D or niacin can irritate your stomach, causing nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal cramps.
- Headaches and dizziness: Excessive amounts of B vitamins, especially B3 and B6, may lead to headaches, dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Fatigue and weakness: High doses of certain vitamins like A, D, E and K can sap your energy, make you feel lethargic or weak.
- Muscle and joint pain: Too much vitamin D can cause muscle aches, pains and weakness. Excess B6 may lead to pain, numbness or difficulty walking.
- Insomnia and irritability: Large amounts of B vitamins, especially B6 and B12, can disrupt your sleep, make it hard to fall asleep or cause irritability and mood changes.
- Liver or kidney damage: Extremely high doses of the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K in particular can build up in your body and damage your liver, kidneys or other organs over time. See a doctor right away if you experience symptoms like dark urine, jaundice or swelling.
The amounts that can lead to an overdose vary depending on factors like your age, weight, overall health and the vitamin in question. So while vitamins are important for wellness in appropriate amounts, be very careful about consuming too many and watch out for these overdose signs. If you experience severe or persistent symptoms, seek medical care immediately. It’s always a good idea to talk to your doctor before supplementing with high doses of any vitamin.
How to Prevent Vitamin Toxicity
To avoid vitamin toxicity, the key is moderation and balance. Too much of any vitamin can be harmful, even if it's a water-soluble vitamin that your body excretes in urine. Some tips to prevent too high of vitamin levels:
Don't mega-dose supplements
Megadoses of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K in particular can build up in your body and cause toxicity. Only take supplements in the recommended amounts. Get most of your vitamins from whole foods instead of pills when possible.Watch out for interactions
Some medications can interact with vitamin supplements and increase your risk of toxicity. Talk to your doctor about any supplements you're taking to avoid dangerous interactions.Limit certain foods
While most people should aim for lots of fruits and veggies, some foods very high in certain vitamins should only be eaten in moderation. For example, liver, which is high in vitamin A, should only be eaten occasionally to avoid excess vitamin A. Cod liver oil supplements should also only be taken as directed.Monitor your levels
If you have a medical condition or restricted diet that makes you prone to vitamin deficiencies or excesses, ask your doctor to test your vitamin levels. Simple blood tests can check for adequate or high amounts of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E and K as well as some water-soluble B vitamins. Catching high levels early can help prevent toxicity.Balance your diet
The healthiest approach is to get a balance of all vitamins by following an overall balanced diet with lots of whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. A balanced diet makes it less likely you'll end up with too much or too little of any vitamin. Focus on the big picture for the best nutrition.
By being aware of these tips to prevent excess vitamin accumulation and maintaining an balanced diet and lifestyle, you can enjoy the benefits of vitamins without the risk of toxicity. Moderation and prudence are key.
Who's at Risk for Vitamin Overdose?
Some people are more at risk of vitamin overdose than others. Several factors can increase your chance of getting too much of a good thing.

Age
As we get older, our bodies often absorb and process vitamins less efficiently. This is especially true for fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E and K that are stored in the body. The kidneys also tend to function less effectively as we age, making it harder to flush out excess water-soluble vitamins like C and B. Older adults are often more likely to take multiple medications and supplements too, raising the risk of unsafe interactions and overdose.Medical conditions
Certain health conditions can impact how your body handles vitamins and minerals. People with liver or kidney disease or damage may have trouble breaking down or eliminating excess vitamins. Gastrointestinal issues like celiac disease or gastric bypass surgery can also hinder absorption and increase the chance of overdose from supplements.Supplement use
While dietary vitamins from whole foods pose little risk, synthetic forms found in some supplements are more likely to lead to overdose when taken in large doses. Single vitamin supplements, especially when taken in high amounts, are more dangerous than balanced multivitamins. Always follow the dosage instructions and don't assume that more is better.Lifestyle
Smoking, heavy alcohol use and unhealthy diets can negatively impact your health, absorption and body's ability to process nutrients. If you smoke or drink regularly, be especially cautious with any vitamin supplements to avoid potential overdose or interactions. A balanced diet with lots of whole foods is the safest way to get the vitamins you need. Only supplement when diet alone cannot provide adequate nutrition.
By being aware of the factors that can influence your vitamin needs and risk of overdose, you can make safer and healthier choices. Moderation and balance are key. Talk to your doctor before taking any supplements to determine what's right for your unique situation. Your age, medical conditions and lifestyle habits are all important considerations for optimal nutrition and wellness.
So in summary, while vitamins are essential for health and wellness, you absolutely can overdo it. Moderation is key. Don't think that if some is good, more must be better. More is not always better when it comes to vitamins and minerals.
Pay attention to the recommended daily amounts and don't exceed them. Your body can only absorb and use so much of any vitamin or mineral. The excess will just pass right through you, providing no benefit. And in some cases, too much of a good thing can actually be harmful to your health.
So do your research, choose a balanced diet and a high-quality multivitamin if needed, but don't go overboard. If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to our team, we are delighted to help you. Stay healthy, my friends!
